Google Takes the Lead in Applying Multicore Fiber Optics to Submarine Cable Systems
Recently, Brian Quigley, Vice President of Global Network Infrastructure at Google Cloud, and Mattia Cantono, Architect of Google Cloud Optical Network, published blog articles introducing the application of multi-core optical fibers in submarine optical cable systems.
The global digitization is accelerating, and the demand for bandwidth is also increasing exponentially. The submarine optical cables that transmit bandwidth between continents must be correspondingly expanded. Therefore, together with industry partners, we have been searching for innovative ways to accommodate more bandwidth per fiber optic cable, improving network resilience and capacity for cloud computing vendors and network operators. Today, we will delve into one of the latest innovations in submarine optical cables: multi-core fiber optic technology.
Firstly, let’s briefly introduce history. The power equipment for traditional submarine optical cables comes from the shore end. When data is uploaded and transmitted through the cable, a dedicated set of pump lasers amplifies the optical signal of each pair of fibers. In recent years, the Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) technology has emerged by increasing the number of optical fibers in the optical cable, enabling the submarine optical cable system to meet the growing demand, thereby providing higher total capacity at a more cost-effective per bit rate.
But the current SDM technology is beginning to face scalability challenges. If the outer diameter of the optical cable is not expanded, it will be difficult to increase the number of optical fibers in each cable, which will require more materials and greater weight, thus placing a burden on maritime operations and maintenance. In addition, adding optical fibers means significantly longer manufacturing, testing, and maintenance times.
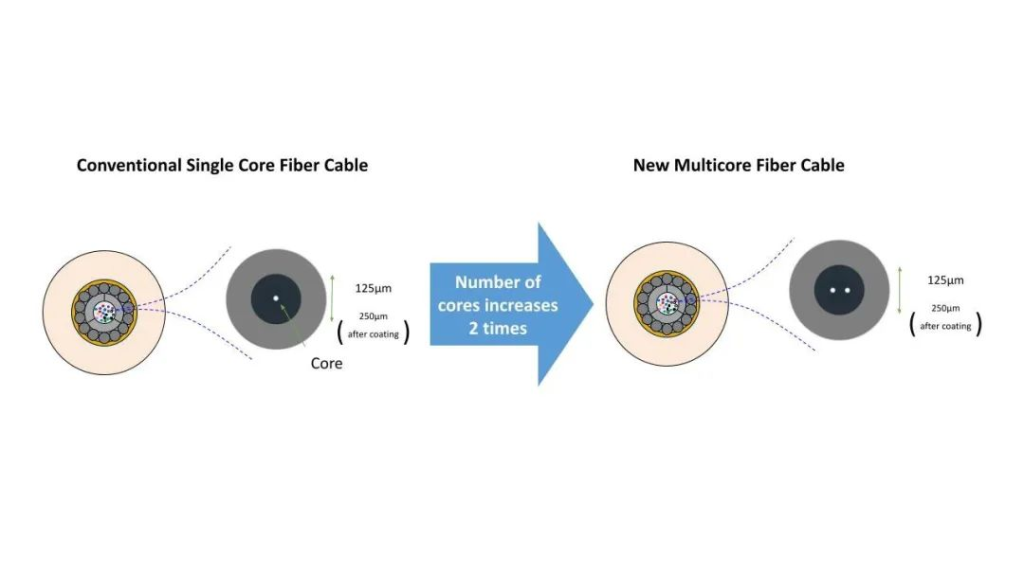
Multi core fiber (MCF) is an evolutionary version of single core fiber, built on the foundation of single core fiber. Single core fiber relies on a circular glass core surrounded by a glass cladding. With MCF, we have doubled the number of cores in the cladding, which means it can transmit more light and information at a lower cost per bit. All of these are implemented in the same fiber! This means that with the same number of cores, fiber optic cables using MCF technology use fewer fibers, thus accelerating manufacturing, testing, and making maintenance easier.
Currently, Google and NEC are collaborating to adopt Multi Core Fiber Optic (MCF) technology to build a new submarine cable system, which is the first time in the submarine cable industry.
Eduardo Mateo, Director of NEC Technology Strategy, stated: “The first implementation of MCF in the submarine network represents an important milestone towards the next generation system, which has larger capacity, more efficient connections, and lower cost per bit.
Over the past decade, Google has worked closely with NEC to promote industry-changing submarine cable technology, and recently introduced MCF into a new submarine cable system, which we are deeply proud of. As single-core optical fibers evolve towards MCF, we look forward to the emergence of a supply chain ecosystem that can provide MCF functionality for the entire industry.
With the increasing demand for online content, cloud services, and Al applications, we expect multi-core fiber optic to become an important component of global telecommunications infrastructure.This is an exciting new direction for expanding the capacity of submarine optical cables, paving the way for further increasing the number of cores per fiber to meet the bandwidth needs of the industry.
